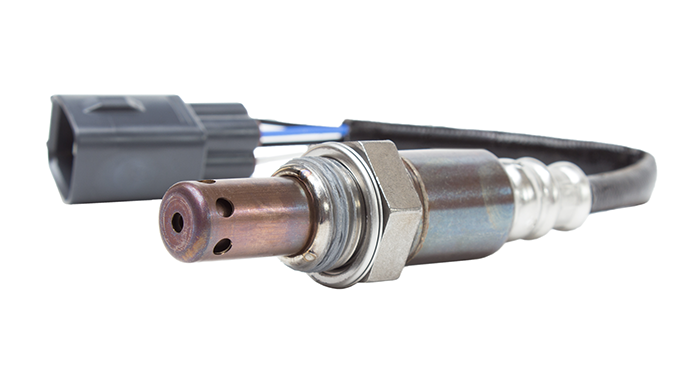
Oxygen sensors are designed to work with your vehicle’s fuel delivery system to ensure optimal performance and fuel efficiency. These devices also referred to as O2 sensors, monitor the emissions or exhaust gas to regulate the air-to-fuel mixture delivered to the engine.
Oxygen Sensor Operation
Your vehicle may use one, two, or more sensors depending on the manufacturer. Sensors are located at points along the exhaust system to measure engine output. The output of the fuel injectors is adjusted according to the information received from one or more oxygen sensors.
Each device takes a reading of the amount of unburnt fuel and oxygen in the exhaust and compares the reading to the normal oxygen level in the air. When a fuel mixture is too rich, less oxygen will be sensed. In this condition, a higher voltage reading is generated. This will create a signal for less fuel to be delivered.
A lean fuel reading, or one that is showing high oxygen content, sends a lower voltage reading. This signals the system to increase fuel delivery. Readings from the sensor are sent to your vehicle’s Engine Control Unit (ECU). The ECU will control how long the fuel injector remains open to deliver fuel.
Your Fuel Pump’s Role
The fuel pump in your vehicle is designed to get the gas from the tank to the fuel injection system. The average injected engine will need to receive 40 psi to 60 psi at the fuel injectors. You need to be aware that electronic fuel pumps are also controlled by the ECU. As a fuel pump wears out, the amount of pressure it delivers can be reduced or erratic. This will result in poor vehicle performance, hesitation, and stalling.
Sensor Failure
An oxygen sensor has a limited lifetime for operation. Sensors can last anywhere from 30,000 to 100,000 miles depending on the type. Symptoms of failure may include rough idling, stalling, or hesitation when accelerating. Many auto part stores have equipment that can test the condition of your oxygen sensors and the rest of the electronic system. A Check Engine light may also be on and the codes from it can be pulled at many local auto parts stores. This can assist in the diagnostic process.
Since sensor failure can mimic a faulty fuel pump, you should have this test completed. You can also have the pressure of your fuel pump tested. Replacing a defective oxygen sensor is less expensive and less time-consuming than replacing a fuel pump, especially when the fuel pump is not the issue.